Why is MAPBM necessary?
Transfusion is one of the most overused procedures in medicine today

Over 50% of transfusions are inappropriate or avoidable

Inexplicable transfusion variability for the same process

Transfusion is a factor that can increase hospital stay, risk of death and infection

The cost of hospital discharges with transfusion is 1.83 times higher and represents 7.8% of the total cost
Reducing over-transfusion is a priority objective for numerous organisations and Right Care initiatives
Institutions
-
World Health Organization
-
European Commission. Directorate General for Health And Food Safety. Health Programme.
-
NHS Blood and Transplant
-
National Blood Authority
Right Care initiatives
-
Ministerio de Sanidad – Compromiso por la Calidad de las Sociedades Científicas
- http://www.msssi.gob.es/organizacion/sns/planCalidadSNS/cal_sscc.htm
- http://www.msssi.gob.es/organizacion/sns/planCalidadSNS/pdf/SOCIEDAD_ESP_ANEST_REA_TE_DOLOR_0K.pdf
- http://www.msssi.gob.es/organizacion/sns/planCalidadSNS/pdf/SOCIEDAD_ESP_HEMATOLOGIA_HEMOTERAPIA_0K.pdf
- http://www.msssi.gob.es/organizacion/sns/planCalidadSNS/pdf/SOCIEDAD_ESP_MIC_UNIDCORONARIAS_0K.pdf
-
Choosing wisely
Guías y consensos
-
Documento «Sevilla» de Consenso sobre Alternativas a la Transfusión de Sangre Alogénica
-
Network for the Advancement of Patient Blood Management, Haemostasis and Thrombosis (NATA)
-
Society for the Advancement of Blood Management (SABM)
La implementación de programas de Patient Blood Management (PBM) en las organizaciones sanitarias es una recomendación de la OMS, Sociedades Científicas y Organismos Gubernamentales para mejorar las prácticas clínicas y resultados en procedimientos donde la práctica transfusional es prevalente
PBM
PBM is recognised around the world as the best strategy for preventing avoidable, unnecessary transfusions.
PBM (Patient Blood Management, previously Blood Saving Program) is a multimodal plan based around patients with the aim of minimising or preventing unnecessary transfusion, and thus improving their clinical evolution.
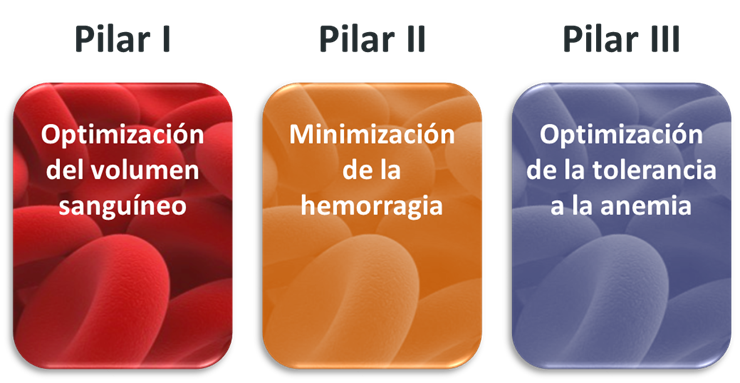
It is based on 3 fundamental pillars:
Current challenges to including PBM as a Standard of care in hospital quality policy

Doctors and nurses are unaware of the real risks associated with transfusion over the medium to long term.

There is little knowledge in health centres about variability in transfusion practice or PBM and their impact on safety.

A PBM program is transversal across the entire organisation, and represents a transformation of organisational culture. It requires a collective approach by clinics, managers and regulators.

Hospitals interested in carrying out a PBM program do not possess the information and methodology concerning what is required, how to begin and how to carry it out.