What is MAPBM?
MAPBM Project
MAPBM was devised in 2014 to help hospitals to tailor their clinical practice so as to reduce unnecessary or avoidable transfusions and thereby to improve results in health.
Patient Blood Management (PBM) is the best strategy for preventing or avoiding over-transfusion in hospitals, and it has been recommended by the WHO since 2010, and by the European Union since 2017. When a PBM program is launched, it is transversal throughout the whole organisation, and it represents a transformation of organisational culture.
Objectives
An assessment model developed for use by a Hospital or Health Service which enables users to:

Identify transfusion variability by procedures.

Assess the maturity of current clinical practices to prevent OVER-transfusion.

Facilitate the implementation of the different components of a PBM program.

Ensure continuous assessment of clinical processes, transfusion results and clinical evolution.

Monitor the levels of implementation and scope of their PBM programs.

Compare with other Health Centres (benchmarking).

Encourage communication between the medical teams and the management with regard to the implementation of PBM and the monitoring of results.
Maturity Assessment Model
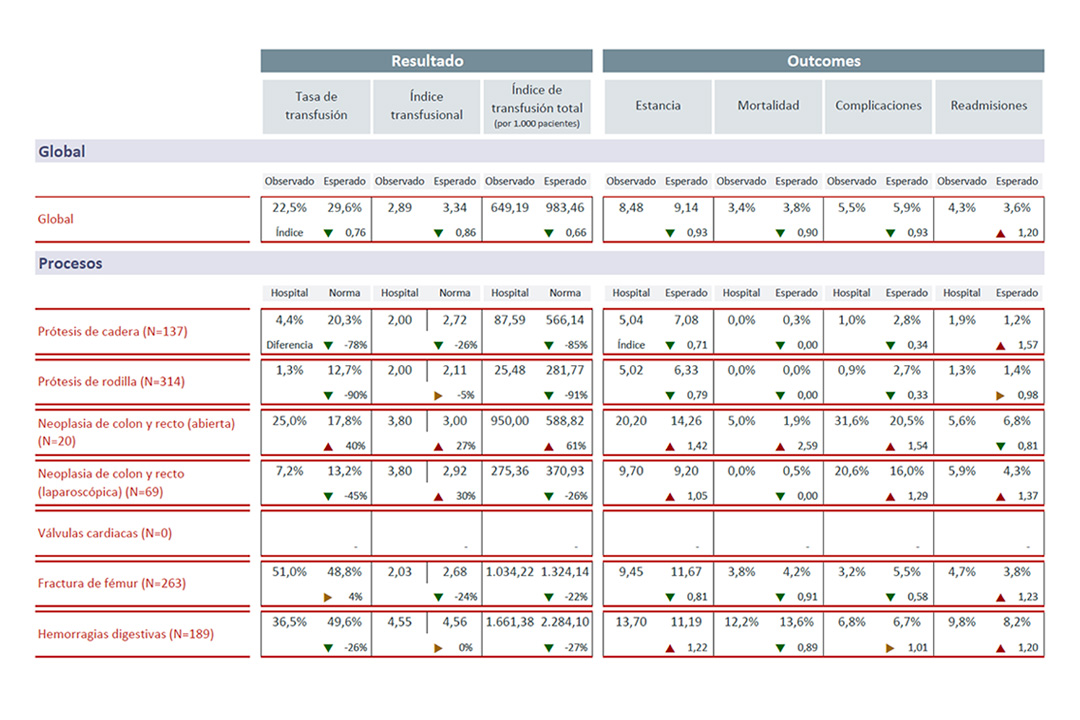
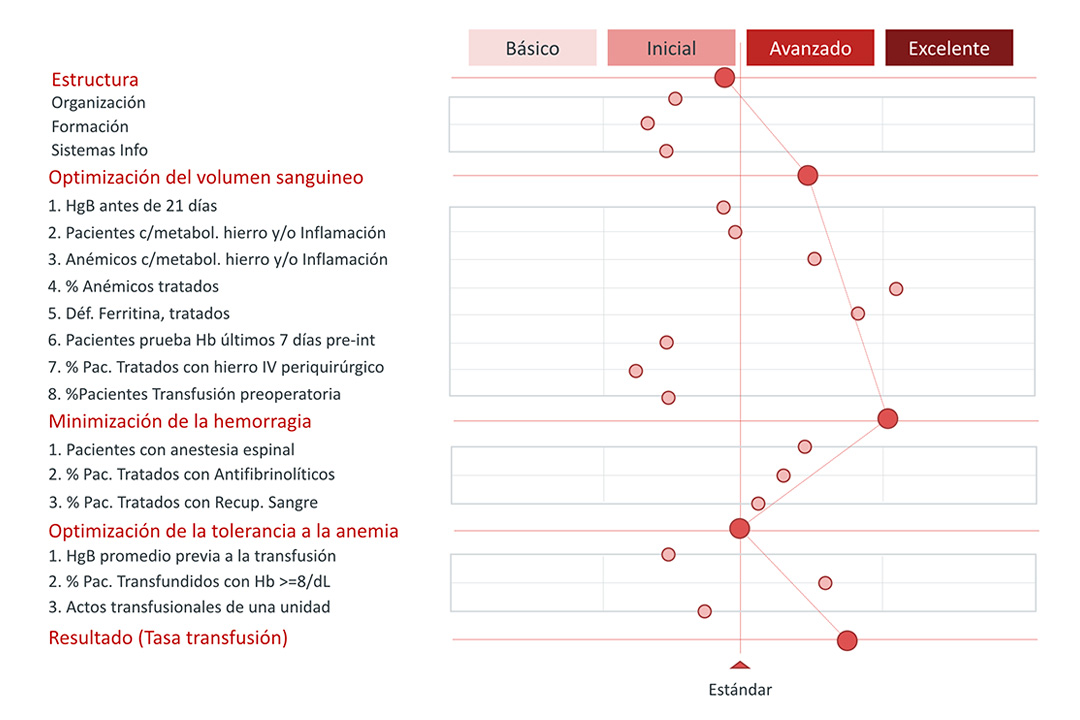
The analysis model is based on a maturation matrix that includes the four aspects that are necessary for all transformation processes – organisation, training, technology and processes – structured into a ‘control panel’ that shows the main PBM quality indicators, related with the transfusion results and outcomes.
-
Structural:
- Organisation
- Training
- Information systems
-
Processes:
- These are based on the three pillars of PBM, applied in 5 intensive procedures on consumption of packed red blood cells
- Adjusted transfusion rate and index
- Outcomes (mortality, stay, complications, re-entries within 30 days)
Maturity is classified into four stages: Basic, Initial, Advanced, Excellent
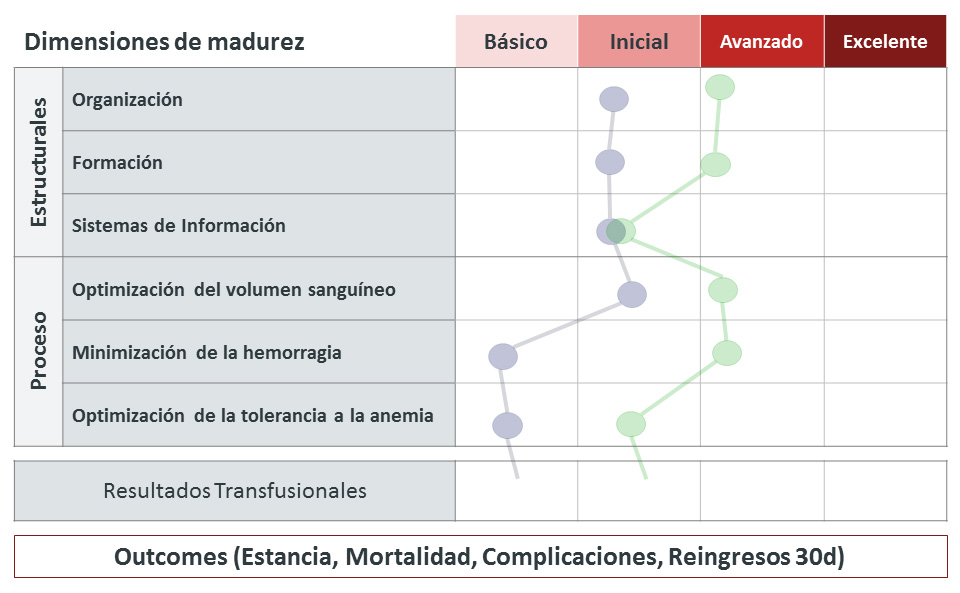
Methodology of assessment cycles
